
He discovered that the wavelength of the reflected x rays decreased in a regular, predictable pattern with increasing atomic mass.
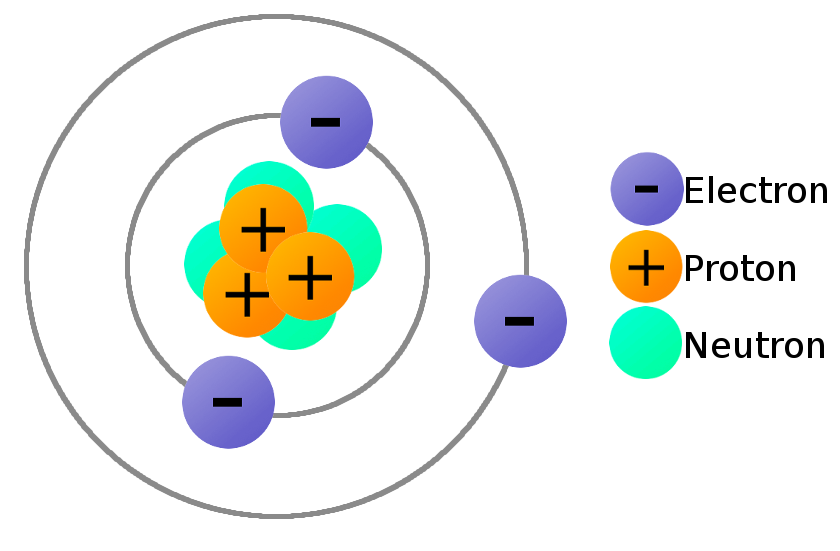
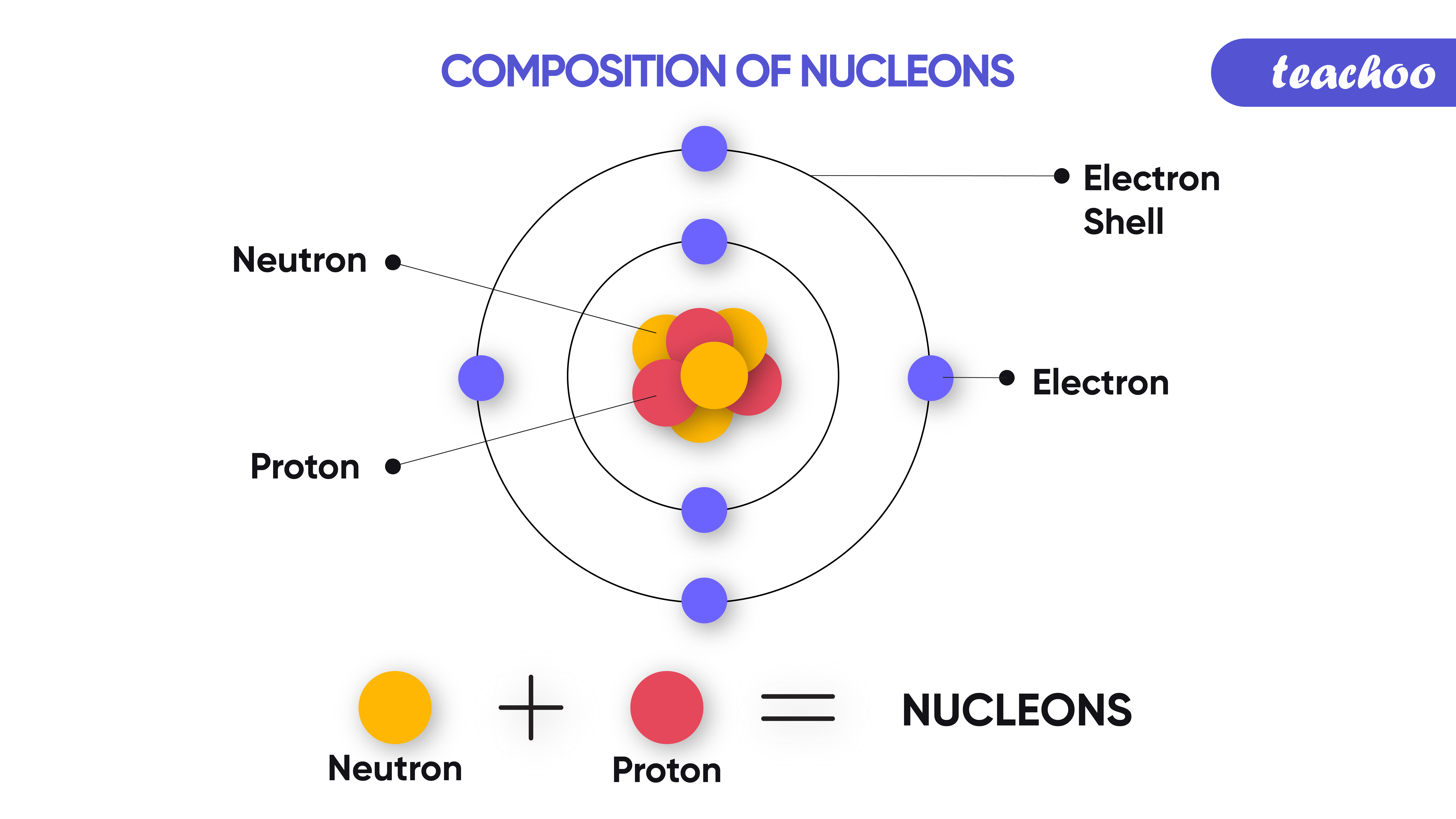
Moseley bombarded a number of chemical elements with x rays and observed the pattern formed by the reflected rays. The concept of atomic numbers evolved from the historical research of Henry Gwyn-Jeffreys Moseley in the 1910s. The numbers of electrons = atomic number. However, To calculate the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom, use its atomic number and mass number: numbers of protons = atomic number. The symbol for an atom can be written to show its mass number at the top, and its atomic number at the bottom. The atomic Number of Na atom = Number of electrons = Number of protons = 11. The atom’s atomic number is equal to the numbers of protons in the nucleus of an atom or the numbers of electrons in an electrically neutral atom.įor example, in a sodium atom, there are 11 electrons and 11 protons.

Atoms of each element contain a characteristic number of protons.In the symbol representing a particular nuclear or atomic species, the atomic number may be indicated as a left subscript.Working with elements from aluminum (which has an atomic number thirteen) to gold (seventy nine), he was able to show that the frequency of these transitions increased with each element studied. Moseley was able to confirm these two hypotheses through experimentation, measuring the wavelengths of photon transitions of various elements while they were inside an x-ray tube. The Bohr model of the atom had the central charge contained in its core, with its electrons circulating it in orbit, much like how the planet in the solar system orbit the sun. Two years later, Henry Moseley and Niels Bohr made further contributions that helped to confirm this. Antonius van den Broek added to this by formerly suggesting that the central charge and number of electrons were equal. This central charge would be roughly equal to half of the atoms total atomic weight. It was he who first suggested the model for an atom where the majority of its mass and positive charge was contained in a core. The atomic number of an element never changes, meaning that the number of protons in the nucleus of every atom in an element is always the same.Īrranging elements based on their atomic weight began with Ernest Rutherford in 1911. Oxygen atoms contain 8 protons and have an atomic number of 8, and so on. All carbon atoms contain six protons and therefore have an atomic number of 6. For example, Hydrogen atoms, which have one proton in their nucleuses, are given an atomic number of one.
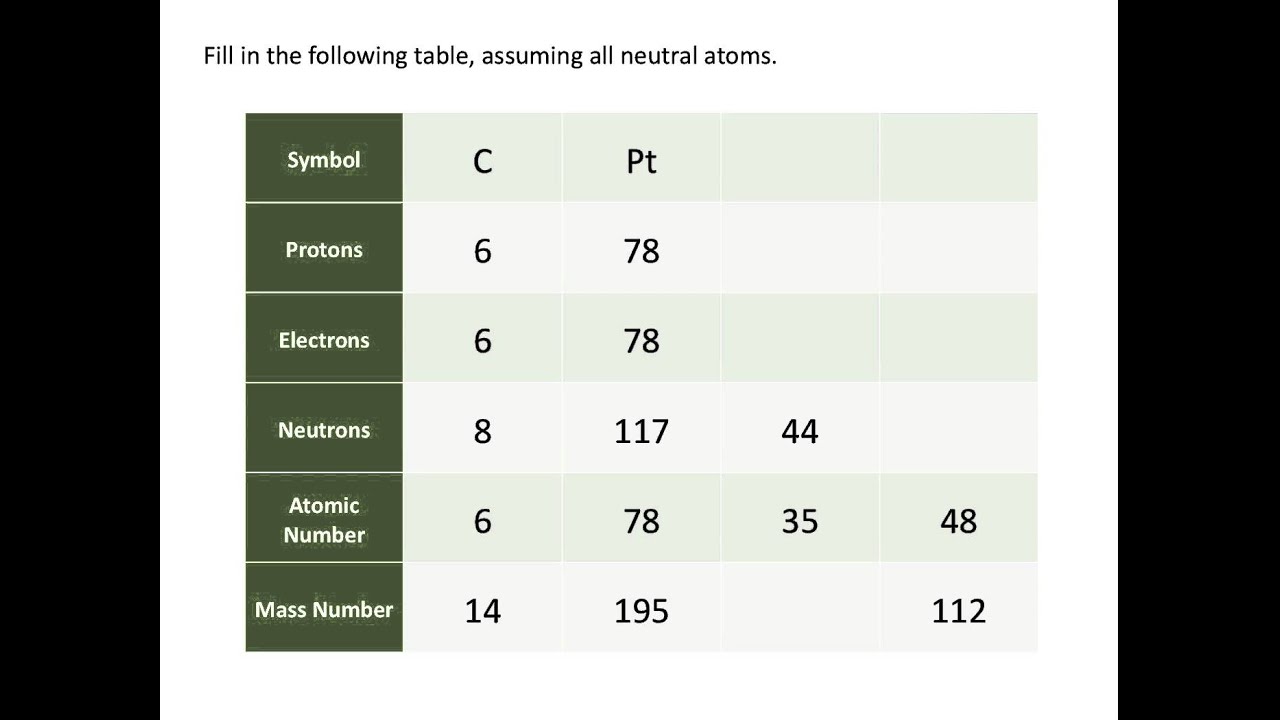
Ever wonder why the periodic table of elements is organized the way it is? Why, for example, does Hydrogen come first? And just what are these numbers that are used to sort them all? They are known as the element’s atomic number, and in the periodic table of elements, the atomic number of an element is the same as the number of protons contained within its nucleus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
